|
Theory of
operation of the Air Conditioning system |
|
The car's air conditioner is a marriage between car heating and the
refrigeration fluid circulation. This enables the creation of controlled
climate conditions, completely independent of exterior conditions.
Therefore this climate system is a true contribution t safety and
comfort in driving.
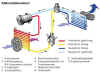
The refrigerant circulation |
|
The refrigerant circulation. Click on the picture icon to expand. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In the compressor the
gas state refrigerant is compressed and thus seriously heated. Under
high pressure it is pressed into the condensor. Here heat is taken
from the gas, and the gas condensates into the fluid state. The dryer, the next station, separates contamination, air bubbles and water from the refrigerant fluid. This way the effectiveness of the system is ensured and components are protected against damage by any contaminations. Next is the expansion
valve. This valve acts like water dam, keeping a steady pressure on one
side and a regular flow thru the opening in the valve. The fluid expands
when it flows thru the valve under pressure and because of the increase
in volume it absorbs energy from the environment. The expansion valve is
directly positioned before to the evaporator, the expansion happens
inside the evaporator. While the fluid is expanding into gas from again,
heat is taken from the environment. The evaporator is like a small radiator. It cools down to a low temperature and an electrical driven fan circulates air thru the radiator. This heat exchange cools the air that is then entered into the cabin of the car. The radiator has a similar construction as the condenser, having an increased surface by use of small aluminum plates that help the heat exchange. A typical system looses 70 up to 100 grams of refrigerant every year due to diffusion from the hoses, seals and links. The refrigerant is not only responsible for the cooling but also lubricates the compressor. Its important that there is always enough refrigerant in the system to ensure the lubrication and prevent any damage and wear of the compressor. Humidity is the enemy of the refrigerant system. The dryer does not only serve as filter contaminations but also to absorb water. It can absorb 6 to 12 grams of water from the refrigerant. It needs to be replaced by a (sealed) new one to ensure proper operation whenever the system is serviced. During a AC system service the system is evacuated, cleaned, and then pressurized at 10 bar using Nitrogen to locate any leaks. Then the system is refilled with the refrigerant taken from it and topped up to the required amount.
Some pricing:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||